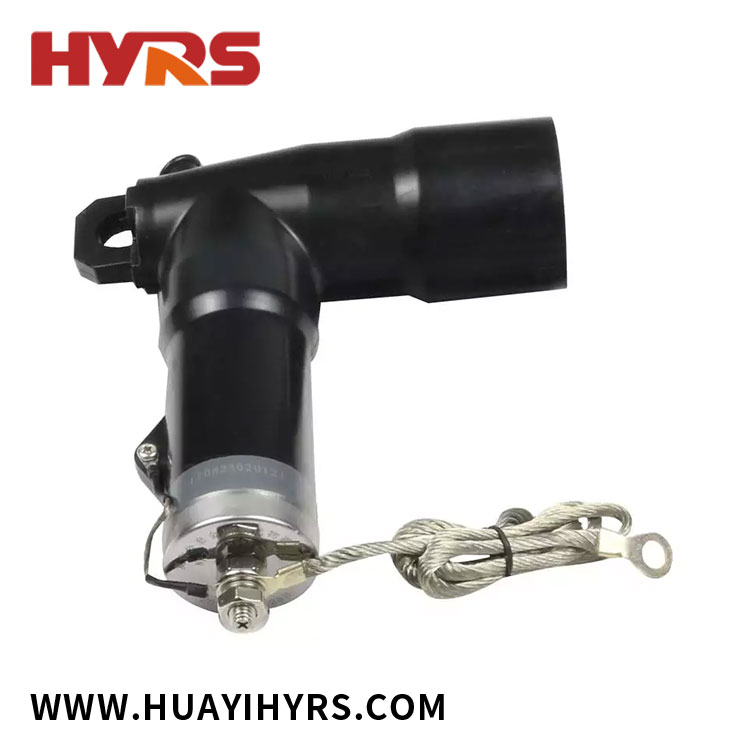
How to Choose the Right Elbow Connector?
2025-08-20
Elbow connectors are critical components in piping and tubing systems, designed to change the direction of flow between two sections of pipe or tube. Whether used in plumbing, hydraulic systems, pneumatic lines, or industrial manufacturing, these connectors ensure fluid, gas, or air moves efficiently through the system while minimizing pressure loss. Selecting the right elbow connector requires understanding materials, sizes, angles, and applications.
An elbow connector typically comes in two common bend angles:
-
45-degree elbow connectors – used when a slight directional change is required without excessive turbulence.
-
90-degree elbow connectors – used when the system needs a right-angle turn for space optimization or routing purposes.
Why Elbow Connectors Are Essential
-
Optimize System Layout – By enabling directional changes, elbow connectors allow more compact and efficient designs.
-
Improve Flow Efficiency – Properly selected connectors reduce turbulence and prevent flow bottlenecks.
-
Enhance Durability – High-quality materials withstand extreme pressures and harsh environments.
-
Reduce Maintenance Costs – Well-designed connectors lower wear and tear on the overall system.
Applications Across Industries
Elbow connectors are used in a wide range of industries:
-
Automotive – Fuel lines, brake systems, and cooling systems.
-
HVAC – Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning pipelines.
-
Oil & Gas – High-pressure pipelines and offshore drilling.
-
Manufacturing – Hydraulic presses, CNC machinery, and assembly lines.
-
Medical Equipment – Precision fluid handling systems.
Understanding these applications is the first step to selecting the right connector. The next step is identifying the key specifications that match your system’s requirements.
How to Select the Right Elbow Connector: Key Specifications
Choosing the correct elbow connector requires evaluating multiple factors, including material compatibility, size, pressure rating, temperature range, and fitting type. Below is a detailed breakdown of the most important specifications.
Material Options
| Material | Best For | Temperature Range | Corrosion Resistance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Brass | Plumbing, air compressors, fuel lines | -40°C to 200°C | High |
| Stainless Steel (SS304/SS316) | Chemical processing, marine systems, high-pressure hydraulics | -50°C to 400°C | Excellent |
| Plastic (Nylon, PVC, PEEK) | Low-pressure water, medical devices, light-duty pneumatics | 0°C to 100°C | Moderate |
| Carbon Steel | Heavy-duty hydraulic and industrial equipment | -20°C to 350°C | Medium |
| Copper | Refrigeration, HVAC, and heat exchange systems | -60°C to 150°C | High |
Angle and Flow Requirements
-
45° Elbow: Best when smooth directional changes are needed to maintain fluid velocity.
-
90° Elbow: Ideal when compact routing is necessary but may create slightly higher pressure drops.
-
Custom Bends: Some industries require 37° or 60° bends for specialized designs.
Pressure and Temperature Ratings
Elbow connectors must match the system’s pressure and temperature specifications:
-
Low-pressure systems (≤150 PSI): Suitable for domestic plumbing and light pneumatics.
-
Medium-pressure systems (150–1500 PSI): Used in automotive, HVAC, and moderate hydraulic systems.
-
High-pressure systems (≥1500 PSI): Found in oil & gas, aerospace, and heavy machinery.
Connection Types
Elbow connectors come in several fitting styles to suit different assembly methods:
-
Threaded – Widely used in plumbing and gas lines; easy to install and replace.
-
Compression – Provides a secure seal for pneumatic and hydraulic applications.
-
Push-to-connect – Popular in air and water systems due to quick installation.
-
Welded – Ensures maximum strength for high-pressure and critical applications.
Product Parameters
| Specification | Details |
|---|---|
| Material | Stainless Steel / Brass / Nylon |
| Bend Angle | 45° / 90° / Custom |
| Thread Type | NPT / BSP / Metric |
| Pressure Rating | Up to 6000 PSI |
| Temperature Range | -50°C to 400°C |
| Sizes Available | 1/8” to 2” |
| Surface Finish | Polished / Passivated / Coated |
Common Challenges and How Elbow Connectors Solve Them
Choosing the wrong elbow connector can lead to system inefficiencies, costly leaks, and frequent downtime. Here are some typical problems and how the right selection prevents them:
Problem 1: Pressure Drops
-
Cause: Using a sharp-angled connector in high-flow systems.
-
Solution: Opt for long-radius elbows to reduce turbulence and maintain velocity.
Problem 2: Material Incompatibility
-
Cause: Mixing metals or using incompatible plastics.
-
Solution: Always match the material with the transported medium to prevent corrosion or chemical reactions.
Problem 3: Temperature Extremes
-
Cause: Using low-temperature-rated materials in high-heat environments.
-
Solution: Select stainless steel or heat-resistant polymers when operating above 200°C.
Problem 4: Tight Installation Spaces
-
Cause: System designs requiring multiple bends in confined areas.
-
Solution: Choose compact elbow connectors or custom bends to optimize routing without sacrificing performance.
FAQs and Final Recommendations
FAQ 1: How do I know which elbow connector material is best for my system?
Answer: Start by identifying the fluid or gas type, operating pressure, and temperature range.
-
For corrosive fluids → Use stainless steel or PEEK.
-
For high-pressure hydraulics → Opt for carbon steel or SS316.
-
For lightweight pneumatic systems → Choose nylon or PVC.
Always ensure the chosen material is compatible with both the medium and the environment.
FAQ 2: Can I use a 90-degree elbow connector instead of a 45-degree one?
Answer: Yes, but you should consider the impact on flow efficiency:
-
90° elbows save space but may cause higher pressure drops due to abrupt directional changes.
-
45° elbows maintain smoother flow but require more space for routing.
If your system is sensitive to turbulence, use long-radius 90° elbows or prefer 45° bends.
HUAYI – Your Trusted Elbow Connector Supplier
Selecting the right elbow connector is crucial for maintaining system performance, efficiency, and durability. By considering material, angle, pressure rating, temperature range, and connection type, you can ensure your system operates smoothly under any conditions.
At HUAYI, we specialize in manufacturing high-quality elbow connectors designed for plumbing, hydraulic, pneumatic, and industrial applications. With strict quality control, advanced production techniques, and customizable options, we deliver solutions tailored to your specific needs.
If you need expert advice or want to explore our extensive product range, contact us today and let HUAYI help you find the perfect connector for your system.