The Ultimate Guide to Washers: Types, Uses, and Choosing the Right One
2024-09-14
In the world of hardware and machinery, washers may seem like small, insignificant parts, but their role is crucial. Whether you're working on a DIY project, assembling furniture, or repairing machinery, washers play a key role in ensuring the strength and stability of bolted joints. Understanding the different types of washers and their functions can help you choose the right one for your next project.
In this blog, we'll dive into the world of washers, exploring their types, uses, and the factors to consider when selecting the right washer for your needs.
What is a Washer?
A washer is a thin, disk-shaped plate with a hole in the middle, typically used to distribute the load of a threaded fastener like a bolt or nut. Washers serve several purposes:
- Distributing Load: They help spread the pressure from the fastener over a larger surface area, preventing damage to the material being fastened.
- Preventing Loosening: Washers can help prevent fasteners from loosening over time, especially in cases where vibration or movement occurs.
- Reducing Friction: They reduce friction between the fastener and the surface, making it easier to tighten or loosen the fastener without damaging the material.
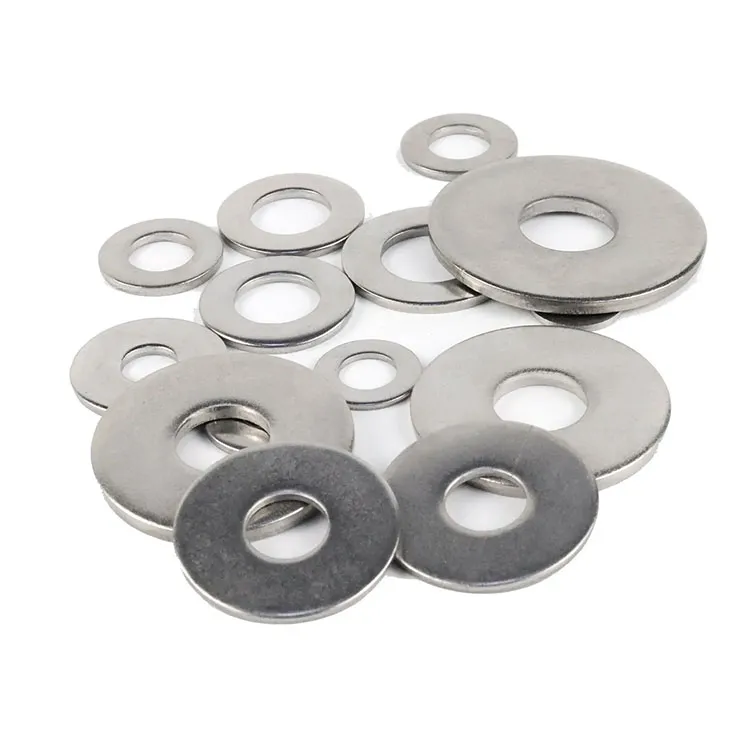
Common Types of Washers
There are several types of washers, each designed for specific applications and conditions. Here are some of the most common types:
1. Flat Washers
Flat washers are the most basic and commonly used type of washer. Their purpose is to spread the load of a bolt or screw over a larger surface area, reducing the risk of damage to the material. They also help prevent the fastener from loosening. Flat washers are used in a wide variety of applications, from furniture assembly to automotive repair.
2. Spring Washers (Lock Washers)
Spring washers, also known as lock washers, are designed to prevent bolts or nuts from loosening due to vibration or movement. They have a slight curve or split that allows them to apply tension when the fastener is tightened. This tension helps hold the bolt in place. Spring washers are commonly used in automotive, aerospace, and machinery applications where vibration is a concern.
3. Fender Washers
Fender washers are similar to flat washers but have a much larger diameter. The increased surface area allows them to spread the load over an even larger area, making them ideal for use in soft or thin materials that might otherwise be damaged by the fastener. Fender washers are often used in automotive and sheet metal work.
4. Shoulder Washers
Shoulder washers, also called insulating or sleeve washers, have a central shoulder that acts as an insulator. They are commonly used in electrical applications to prevent metal fasteners from coming into contact with electrical components, reducing the risk of short circuits.
5. Countersunk Washers
Countersunk washers are used with countersunk screws, which have heads that taper down to the surface of the material. The washer fits snugly into the countersink hole, allowing the screw to sit flush with the surface. This type of washer is used in applications where a smooth, flat surface is important, such as in cabinetry or fine woodworking.
6. Sealing Washers
Sealing washers, often made from materials like rubber or silicone, are used to create a watertight or airtight seal. They are commonly used in plumbing, roofing, and applications where moisture or gas sealing is required. Sealing washers help prevent leaks and protect materials from corrosion or other damage caused by water or air exposure.
7. Star Washers
Star washers, also known as toothed or serrated washers, have jagged edges that dig into the material and the fastener. These washers are designed to provide additional grip, preventing the fastener from loosening due to vibration. Star washers are often used in electrical applications to improve grounding by penetrating the surface for better contact.
Uses of Washers
Washers are used across various industries and for a range of applications, including:
- Construction: Washers are used in building construction to ensure that bolts and screws provide a strong and secure fastening.
- Automotive: In vehicles, washers help reduce vibrations, distribute loads, and protect surfaces from wear and tear.
- Electronics: In electrical assemblies, insulating washers are used to prevent electrical shorts, while lock washers are used to keep connections secure.
- Plumbing: Sealing washers prevent leaks and ensure a tight seal between pipes and fittings.
- Machinery: Washers are used in mechanical assemblies to provide stability, reduce wear, and prevent fasteners from loosening due to movement.

Choosing the Right Washer
Selecting the correct washer for your project is essential for ensuring a secure and long-lasting fastener assembly. Here are some key factors to consider:
1. Material
Washers are made from a variety of materials, each suited for specific applications:
- Stainless Steel: Resistant to rust and corrosion, stainless steel washers are ideal for outdoor and marine applications.
- Brass: Brass washers are often used in plumbing due to their resistance to corrosion and rust.
- Plastic or Nylon: These materials are commonly used for insulating washers in electrical applications or where corrosion resistance is needed.
- Rubber or Silicone: These materials are used in sealing washers to provide a watertight or airtight seal.
2. Size and Thickness
The size of the washer should match the size of the bolt or screw being used. The washer’s thickness should be adequate to handle the load without deforming. For applications involving heavy loads or stress, thicker washers may be necessary.
3. Application Requirements
Consider the environment in which the washer will be used. For example, if the washer will be exposed to moisture or chemicals, corrosion-resistant materials like stainless steel or brass are preferred. If vibration is a concern, lock washers or star washers may be the best choice.
4. Type of Fastener
Different fasteners, such as bolts, screws, or rivets, may require different types of washers. For example, a countersunk screw requires a matching countersunk washer to ensure a flush surface finish.
Conclusion
Washers may be small components, but they play a critical role in ensuring the strength, durability, and stability of fastened joints. By selecting the right type of washer for your project—whether it's a simple flat washer to distribute load or a lock washer to prevent loosening—you can significantly improve the reliability and longevity of your assembly.
Whether you're tackling a DIY project, assembling machinery, or working in construction, understanding washers will help you make more informed choices and achieve better results.