Understanding Diesel Engines: How They Work and Their Advantages
2024-07-11
Diesel engines have long been a staple in various industries, from transportation to construction, due to their durability and efficiency. In this blog, we will explore how diesel engines work, their advantages over other types of engines, and why they continue to be a popular choice for heavy-duty applications.
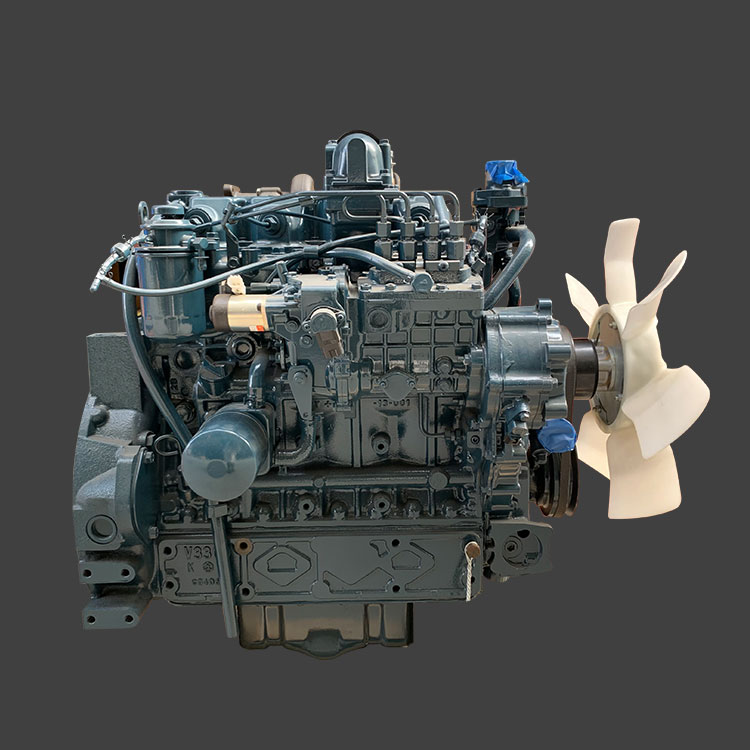
How Diesel Engines Work
Diesel engines operate on the principle of compression ignition rather than spark ignition used in gasoline engines. Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of how a diesel engine works:
1. Intake Stroke: Air is drawn into the cylinder through the intake valve as the piston moves down.
2. Compression Stroke: The intake valve closes, and the piston moves up, compressing the air to a high pressure and temperature.
3. Power Stroke: Fuel is injected into the highly compressed air. The high temperature causes the fuel to ignite spontaneously, creating a powerful explosion that forces the piston down.
4. Exhaust Stroke: The exhaust valve opens, and the piston moves up again, expelling the exhaust gases from the cylinder.
This cycle repeats continuously, providing the power necessary to drive the engine.
Advantages of Diesel Engines
1. Fuel Efficiency: Diesel engines are more fuel-efficient than gasoline engines. Diesel fuel has a higher energy density, meaning it can produce more energy per gallon compared to gasoline. This results in better mileage and lower fuel costs.
2. Torque and Power: Diesel engines produce more torque at lower RPMs, making them ideal for heavy-duty applications such as towing and hauling. This high torque is due to the higher compression ratio and the nature of diesel fuel combustion.
3. Durability and Longevity: Diesel engines are built to withstand higher pressures and temperatures, making them more durable and long-lasting than gasoline engines. They are often used in applications where reliability and longevity are crucial.
4. Lower CO2 Emissions: Diesel engines emit less carbon dioxide (CO2) per unit of energy produced compared to gasoline engines. This makes them a more environmentally friendly option in terms of CO2 emissions.
5. Better Performance in Heavy-Duty Applications: Diesel engines are preferred for commercial vehicles, construction machinery, and industrial equipment due to their superior performance under heavy loads and harsh conditions.
Common Uses of Diesel Engines
1. Commercial Vehicles: Trucks, buses, and other commercial vehicles often use diesel engines due to their fuel efficiency and torque.
2. Industrial Machinery: Construction equipment such as excavators, bulldozers, and cranes rely on diesel engines for their power and reliability.
3. Marine Applications: Ships and boats frequently use diesel engines for their durability and efficiency in long-distance travel.
4. Agricultural Equipment: Tractors and other farming machinery use diesel engines to handle the rigorous demands of agricultural work.
5. Power Generation: Diesel generators are used for backup power and in remote locations where grid power is unavailable.
Conclusion
Diesel engines are a powerful, efficient, and durable option for a wide range of applications. Their fuel efficiency, high torque, and longevity make them a preferred choice for heavy-duty tasks in various industries. Understanding how diesel engines work and their advantages can help you appreciate why they remain a vital technology in our world today.