What is Lost Wax Casting?
2024-10-22
Lost wax casting, also known as investment casting, is an ancient and versatile metalworking technique that has been used for thousands of years to create intricate and detailed metal objects. From fine jewelry to industrial components, lost wax casting is prized for its ability to produce high-precision castings with complex shapes and smooth surfaces. In this blog, we’ll explore the history, process, advantages, and modern applications of this time-tested method.

1. What is Lost Wax Casting?
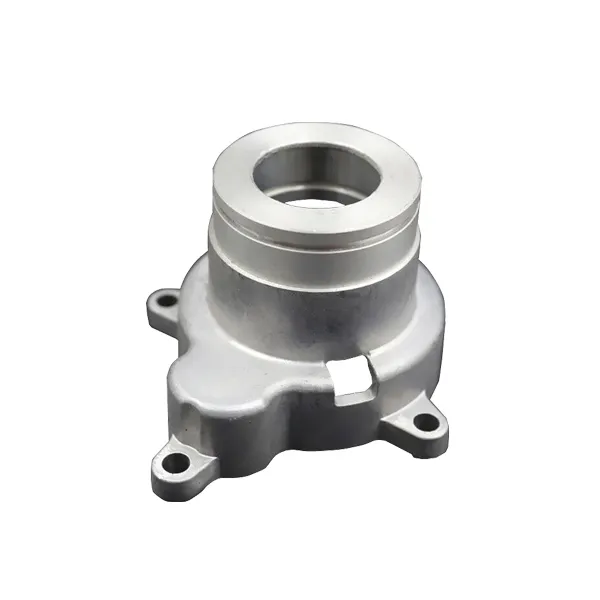
Lost wax casting is a metal casting process in which a wax model of the desired object is created, then coated with a ceramic material to form a mold. Once the mold is hardened, the wax is melted and drained away, leaving behind a hollow cavity that can be filled with molten metal. After the metal cools and solidifies, the ceramic mold is broken away to reveal the finished metal object.
The lost wax casting process is known for its high accuracy, fine details, and ability to reproduce complex geometries. It is widely used in industries like jewelry making, art sculpture, aerospace, automotive, and medical devices due to its precision and versatility.
2. The Lost Wax Casting Process
Lost wax casting involves several detailed steps, each contributing to the overall accuracy and quality of the final cast. Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of the process:
a) Creating the Wax Model
The process begins by making a wax model or pattern of the desired object. The wax model is an exact replica of the final metal product, and it can be crafted by hand or using modern technologies like 3D printing. In some cases, multiple wax models are attached to a central wax "tree" to allow for the casting of several parts at once.
b) Building the Ceramic Mold
Once the wax model is complete, it is coated with a refractory ceramic material. This ceramic shell is applied layer by layer, allowing it to dry and harden after each application. The mold must be strong enough to withstand the heat of the molten metal and durable enough to retain the fine details of the wax model.
c) Wax Removal
After the ceramic mold has fully hardened, the wax is melted and removed by heating the mold in a kiln or autoclave. This is where the process gets its name — the wax is "lost" as it melts and drains away, leaving behind the hollow cavity that will be filled with metal.
d) Pouring the Molten Metal
The ceramic mold, now empty of wax, is heated to a high temperature to prevent it from cracking when the molten metal is poured. The molten metal, whether it’s gold, silver, steel, or another material, is then poured into the mold, filling the cavity left by the wax model.
e) Breaking the Mold
Once the metal has cooled and solidified, the ceramic mold is carefully broken away to reveal the cast metal object inside. This step is often called "investment removal." The object is then cleaned and polished to remove any residual ceramic and improve its surface finish.
f) Finishing Touches
After casting, the metal object may undergo further finishing processes such as grinding, polishing, or machining to achieve the desired final look and tolerances. If necessary, additional details or embellishments can be added at this stage.
3. History of Lost Wax Casting
Lost wax casting is one of the oldest metal casting techniques in the world, with origins dating back over 6,000 years. It was first used in ancient civilizations such as Mesopotamia, Egypt, China, and the Indus Valley, where artisans used the technique to create decorative items, religious artifacts, and tools.
In ancient times, the method was primarily used to cast small objects like jewelry, figurines, and weaponry. The famous Benin Bronzes of West Africa, the intricate gold jewelry of the Incas, and many Renaissance sculptures were all created using lost wax casting.
Over the centuries, the process has been refined and adapted for modern industrial applications, but its fundamental principles remain largely unchanged. Today, lost wax casting continues to be a preferred method for creating highly detailed and precise metal parts.
4. Advantages of Lost Wax Casting
Lost wax casting offers numerous advantages over other casting methods, making it an ideal choice for producing complex, high-precision components. Some key benefits include:
a) Exceptional Detail and Accuracy
Lost wax casting allows for the production of parts with extremely fine details and tight tolerances. This makes it ideal for applications where precision is critical, such as in the aerospace, medical, and jewelry industries.
b) Complex Shapes
The process allows for the creation of intricate and complex shapes that would be difficult or impossible to achieve with traditional machining or other casting methods. This includes parts with internal cavities, undercuts, and intricate surface textures.
c) Smooth Surface Finish
The ceramic mold captures even the smallest details of the wax model, resulting in castings with a smooth surface finish. This reduces the need for extensive post-processing or finishing, saving time and labor.
d) Material Versatility
Lost wax casting can be used with a wide range of metals and alloys, including gold, silver, bronze, aluminum, stainless steel, and titanium. This makes it a versatile process suitable for a variety of industries and applications.
e) Minimal Material Waste
Since the wax model is precisely crafted to the desired dimensions, there is minimal material waste during the casting process. This can result in significant cost savings, especially when casting expensive materials like precious metals.
5. Applications of Lost Wax Casting
Lost wax casting is used in a wide range of industries, from art and jewelry to high-tech manufacturing. Some of the most common applications include:
a) Jewelry Making
Lost wax casting is widely used in the jewelry industry to create finely detailed pieces, including rings, necklaces, bracelets, and pendants. The process allows jewelers to produce intricate designs with high precision.
b) Art and Sculpture
Artists and sculptors use lost wax casting to create detailed bronze sculptures and other metal artworks. The ability to reproduce intricate details makes it a popular choice for fine art castings.
c) Aerospace and Automotive Components
In the aerospace and automotive industries, lost wax casting is used to produce high-precision components such as turbine blades, engine parts, and exhaust systems. The process’s ability to create complex, lightweight, and durable parts is highly valued in these industries.
d) Medical Devices
The medical industry uses lost wax casting to manufacture surgical instruments, dental implants, and prosthetic devices. The process's precision ensures that these critical components meet strict performance and safety standards.
6. Modern Innovations in Lost Wax Casting
While the basic principles of lost wax casting have remained unchanged for centuries, modern innovations have enhanced the efficiency and precision of the process. Some recent developments include:
- 3D Printing: Advances in 3D printing technology have revolutionized the creation of wax models, allowing for greater design flexibility and accuracy. 3D-printed models can be used directly in the lost wax casting process, speeding up production and reducing costs.
- Automation: In large-scale industrial applications, automation has been integrated into various stages of the lost wax casting process, from model creation to mold building and metal pouring. This increases production speed and consistency.